My lab has an Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS server on which Veeam’s Salesforce environment protection software (Veeam Backup for Salesforce) is installed.
During the monthly operation of updating the operating system, some errors appeared that did not allow me to complete the operation.
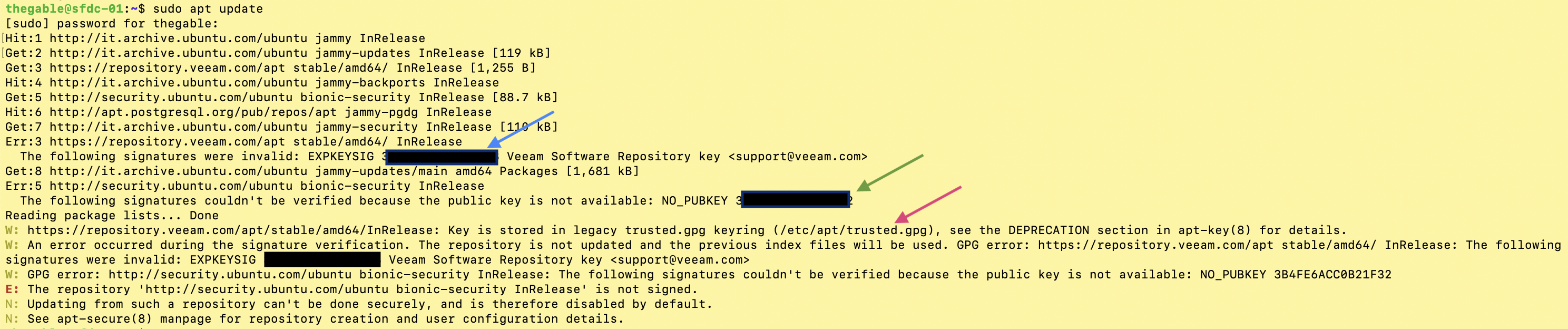
The ‘output of the “sudo apt update” command, showed three errors highlighted in image 1 with the blue, green, and red arrows.
 Picture 1
Picture 1
1. The first, (blue arrow) indicated that the digital signature linked to the Veeam repository (“https://repository.veeam.com/apt stable/amd64/ In Release”) was no longer valid.
2. The second (green arrow) indicated that the digital signature had also expired for the Ubuntu-security site (“http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-security InRelease”).
3. The third error (actually a warning, red arrow), indicated that the key management methodology named“apt-key” is deprecated recommending the ‘use of a more secure method named “trusted.gpg.d”.
—
Browsing the Internet, I found the solutions that met my needs:
1. The KB2654 on the Veeam website shows how to import a new key. The only real caution is to run the command as the root user (see image 2).
 picture 2
picture 2
2. As shown in ‘image 3, simply request a key update by entering the required identifier at the end of the command in the output of image 1 (green arrow).
 image 3
image 3
Note 1: apt-key is a comado used to manage a gpg key fob for secure apt. The keychain is stored in the file ‘/etc/apt/trusted.gpg’ (not to be confused with the related but not very interesting /etc/apt/trustdb.gpg). The command apt-key can display the keys in the keyring and add or remove keys.
3. The last line of image 4 shows the command that addresses the security warning. It involves copying the keychain (trusted.gpg) inside the trusted.gpg.d folder.
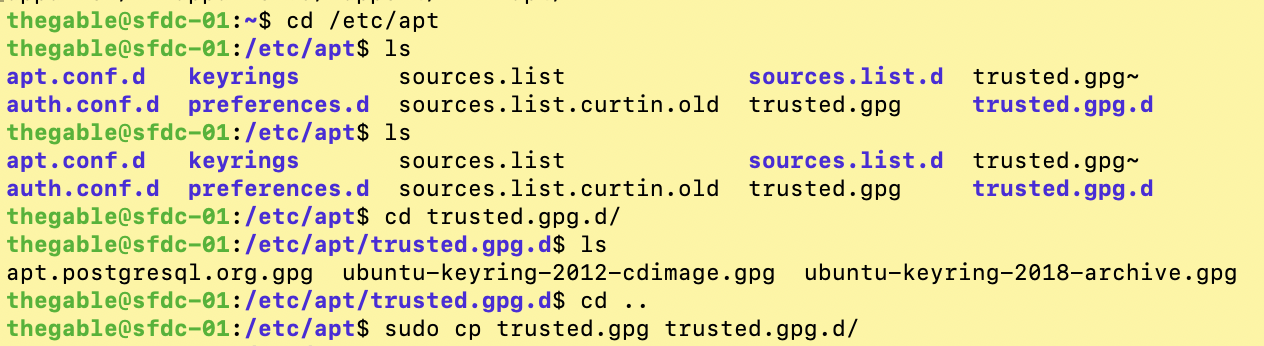 Picture 4
Picture 4
In the article“Handeling the apt-key deprecation” you will find all the details that illustrate the security benefits of the new approach.
Note 2: Veeam Backup for Salesforce has its own mechanism for checking for new product versions and updates.
The same mechanism later allows the necessary software packages to be downloaded and installed.
I remember that these are product updates, not operating system updates.
